Foundation for Efficiency and Innovation
Data interoperability plays a pivotal role in driving innovation by facilitating seamless collaboration and integration across various systems and applications. It enhances efficiency, reduces operational costs, and allows for the aggregation of diverse data sources, leading to more informed decision-making. By fostering scalability and flexibility, interoperability encourages the adoption of new technologies and the development of standards, which are essential for innovation. This process not only enables the creation of novel services and products but also improves user experiences through real-time data exchange and intuitive system interactions. Consequently, data interoperability is a critical component in advancing technological progress and fostering innovative solutions in multiple sectors.
Project 1: Foundational Research in Integrated Building‐IoT Data Standards
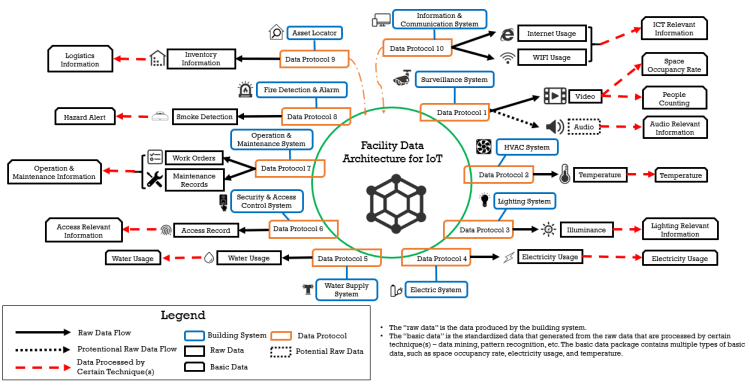
The project focused on achieving data interoperability between building systems and the Internet of Things (IoT). It aimed to integrate IoT data standards with building information standards, enhancing spatial semantics for IoT systems and enriching intelligent building efforts. The research involved collecting and analyzing existing data standards, identifying use cases with industry partners, and proposing a scalable data acquisition framework for smart environments. This framework was intended to utilize data from separate building systems for innovative IoT applications, including smart buildings, communities, and cities. A pilot project demonstrated the feasibility of this federated data framework.
Project Team: Dr. Ray Gao, Dr. Shu Tang, Dr. Pardis Pishdad‐Bozorgi, and Dr. Dennis R Shelden.
Project 2: BIM-assisted Building Automation System information exchange using BACnet and IFC
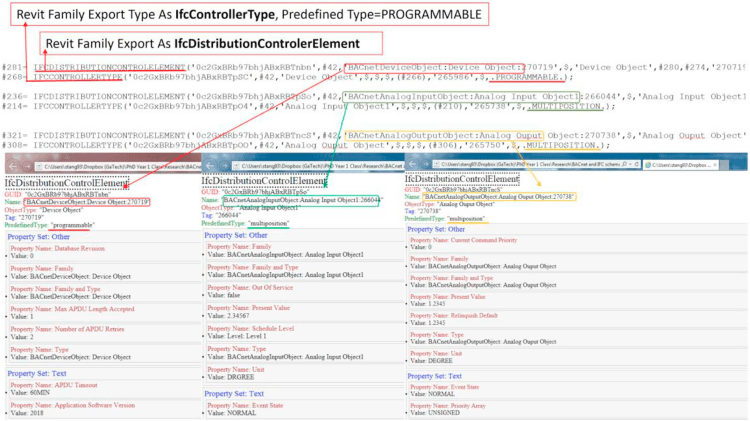
The research team focused on enhancing Building Automation System (BAS) design and operation through the integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Building Automation and Control Networks (BACnet). We utilized Information Delivery Manual (IDM) and Model View Definition (MVD) methodologies to define a subset of the Industry Foundation Class (IFC) schema, enabling BACnet protocol-based BAS information to be represented within the IFC data model. This integration facilitates the exchange of BAS data across various project stages using BIM tools, aiming to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of smart building management.
Project Team: Dr. Shu Tang, Dr. Dennis R Shelden, Dr. Charles M. Eastman, Dr. Pardis Pishdad‐Bozorgi, and Dr. Ray Gao.